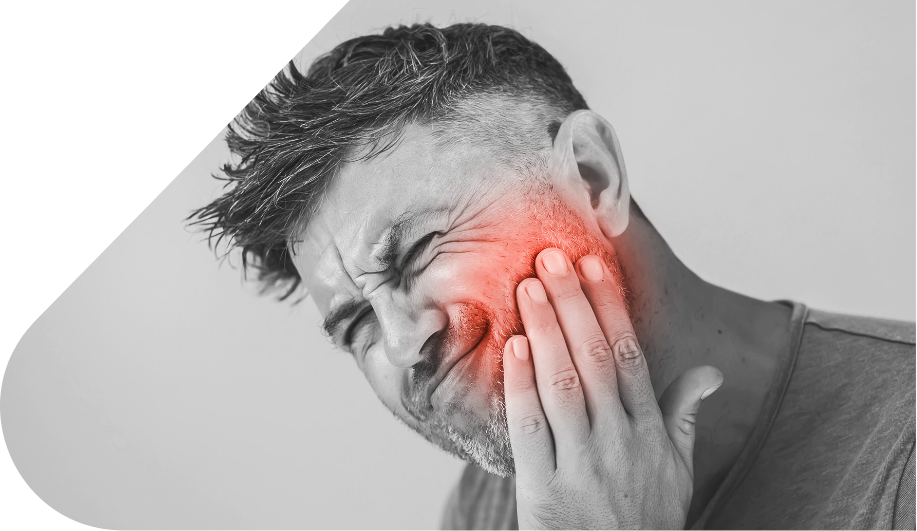
Toothache is a pain that everyone experiences at least once in their life. It arises in the tooth itself or in the surrounding structures, with various possible causes – cavities, injury (fracture), abscess, damage inside the tooth, gum inflammation, and so on.

The pain appears either immediately after the event (in case of trauma) or after some time, often during the night. Night pain is explained by the fact that blood flow to the head increases when lying down. This leads to swelling in the affected area, which in turn raises pressure on the nerve endings in the dental pulp and intensifies the pain sensitivity.
Toothache is a typical somatic, nociceptive pain; therefore, its treatment is based on the principles of managing somatic pain – eliminating the cause and suppressing the pain symptoms.
The removal of the cause of toothache takes into account the anatomy and physiology of the oral cavity. The presence of numerous sensory nerve fibers intensifies the pain sensation. The rich blood supply supports the healing process but can also facilitate the spread of the cause. In cases of inflammation, the characteristics of local innervation and blood circulation contribute to easier transmission of damage to adjacent areas and the addition of neuropathic symptoms to the pain syndrome. This condition requires supplementary treatment.

The oral cavity creates a favorable environment for the growth of numerous microorganisms, which under certain conditions can become pathogenic. The presence, in some people, of spaces between teeth and pockets in the gums (periodontium), combined with poor oral hygiene, further increases the likelihood of developing and chronicizing local infections and related complications — ranging from bad breath and chronic pain to gangrene, granulomas, or tooth loss. Therefore, treatment of the causes of toothache should be carried out under specialist supervision.
For symptomatic pain relief, the use of analgesics is preferred, most commonly from the group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), following the principle of the lowest effective dose. The goal is to quickly and significantly suppress pain while minimizing the occurrence of adverse effects.
Ibuprofen is one of the most widely used analgesic drugs in the world.
Oklys Express and Oklys Forte are innovative pain relief medications. Their active ingredient, ibuprofen L-arginine, allows for rapid absorption of the active substance after oral administration.
Existing studies show that significant pain relief caused by tooth extraction is observed twenty minutes after intake, nearly twice as fast compared to conventional ibuprofen.
* Desjardins P. et al. Ibuprofen arginate provides effective relief from postoperative dental pain with a more rapid onset of action than ibuprofen. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology volume 58, p. 387–394 (2002)